Letter routing templates

To streamline your communication processes, implementing letter routing templates is a key strategy. These templates help structure correspondence efficiently, saving time and reducing errors. Start by selecting a layout that suits your needs–whether for formal business letters or quick internal memos, a clear format is crucial for readability and proper handling.
Ensure that each template includes predefined fields for sender and recipient information, subject lines, and specific routing instructions. This eliminates ambiguity and speeds up the distribution of documents. Use consistent formatting to maintain professionalism and make it easier for recipients to process the information quickly.
Incorporating routing instructions directly into the template simplifies the process of directing letters to the correct department or individual. Automation tools can enhance this step, ensuring that the right person receives the letter without unnecessary delays or confusion. Customize the templates regularly to align with any changes in your workflow or organization structure.
By using letter routing templates, your team can handle correspondence in a more organized manner, leading to fewer miscommunications and faster response times. This practical approach helps maintain order, especially in environments with high document volume.
Here is the corrected text, where word repetition is limited:
To improve clarity and readability, eliminate unnecessary redundancy by using varied language. Instead of repeating the same words, try rephrasing sentences or using synonyms. This will make your writing flow better and keep the reader engaged. Additionally, avoid starting consecutive sentences with the same words. Break up longer sentences into shorter ones when appropriate, and structure your paragraphs logically to ensure smooth transitions between ideas. Limiting repetition doesn’t just reduce monotony; it also enhances the overall quality of the text.
Another strategy is to replace repetitive phrases with concise alternatives that still convey the message clearly. For example, rather than saying “as well as” multiple times, use “and” or restructure the sentence. This approach allows you to keep the content direct without losing meaning. Keep in mind that each word you choose should serve a purpose, whether it’s clarifying a point or adding value to the message.
Lastly, consider using varied sentence structures to break the pattern. A mix of short and long sentences creates a rhythm that maintains reader interest while avoiding the repetitiveness that can bore them. This way, your writing remains dynamic and compelling throughout.
- Letter Routing Templates: Practical Applications and Solutions
Start by creating clear and concise routing templates that address specific needs. For instance, in a business setting, routing templates can be set up to streamline communication across departments, ensuring the right person handles each letter. For a more efficient process, structure templates based on common scenarios like client inquiries, product returns, or internal memos.
Use templates with predefined fields for addresses, departments, and urgency levels to save time. Integrating a color-coding system into your template makes it easy to quickly prioritize letters based on their content, allowing recipients to act without delay. This approach works particularly well in high-volume environments, where quick decision-making is key.
To ensure accuracy, align routing instructions with specific letter types. For example, letters related to legal matters should route directly to the legal team, while financial documents may go to accounting. Having predefined routes reduces errors and unnecessary steps in handling important letters.
Another useful technique is digital routing. Tools like automated workflow software can use routing templates to track and direct digital letters to appropriate personnel. This system minimizes human error and speeds up internal processing by removing manual handling of physical letters. Keep your templates flexible, allowing for easy updates based on departmental changes or shifts in priorities.
For businesses that handle both internal and external correspondence, make use of distinct templates for each. Internal routing templates might include categories like HR, IT, or operations, while external templates could break down by client or partner, providing a more targeted flow. Such organization cuts down on miscommunication and optimizes response time.
Define routing rules that align with the unique needs of each communication channel. This involves selecting specific criteria based on the channel’s function and intended audience.
- Analyze Channel Characteristics: Review the communication method’s requirements, such as email, SMS, or chat. Each channel may have unique features, like length restrictions or urgency requirements.
- Identify Message Components: Break down the message flow into essential elements. For example, in emails, headers, subject lines, and body text may have different routing rules compared to SMS, where character limits matter more.
- Establish Routing Logic: Develop templates with conditional logic. For instance, set up rules that direct urgent emails to high-priority departments or forward automated replies during off-hours.
- Integrate Automation Tools: Use platforms like Zapier or custom APIs to automate routing across various systems. Set predefined conditions to automatically route messages based on specific keywords or sender attributes.
- Test Routing Scenarios: Simulate different scenarios to verify the templates work correctly. Ensure that messages are directed to the right teams or systems based on the established rules.
Customize each template further by considering user preferences or behavior, ensuring messages are routed quickly and efficiently without manual intervention. Fine-tuning and iterative testing are key to maintaining accuracy and performance over time.
Choose a letter routing template that aligns with your organization’s communication style and workflow. Identify whether your team requires a simple, straightforward format or a more detailed, hierarchical approach. For businesses with multiple departments, a template that supports cross-department communication may be most useful. Alternatively, a template that focuses on efficiency and speed will be ideal for smaller teams with limited resources.
Consider the frequency of your letter routing. If your organization sends out routine communications, a standardized template saves time and maintains consistency. For less frequent but critical correspondence, a more tailored template might be needed, ensuring specific information is highlighted effectively.
Review the level of personalization required. If your letters often need customization for different recipients, a flexible template with customizable sections should be prioritized. On the other hand, if uniformity is more important, opt for a template with predefined fields and less need for adjustments.
Lastly, evaluate the integration of the template with existing tools and platforms. If your organization uses specific software for document management or collaboration, ensure that the letter routing template works seamlessly within those systems. This reduces manual intervention and improves overall efficiency.
Integrating routing templates into email systems streamlines the process of directing emails based on specific criteria. Begin by ensuring your email system supports customizable routing rules. Many modern platforms, such as Microsoft Exchange or Gmail for business, have built-in capabilities to handle email routing through templates.
1. Choose a Template Format
Select a routing template format compatible with your email server. Formats like XML or JSON are commonly used for these integrations. These templates define the conditions under which certain emails are redirected, based on attributes like sender, subject, or content keywords.
2. Set Up Routing Rules

- Define conditions for routing. For example, you can route emails from specific domains to a designated department or direct marketing emails to a particular folder.
- Apply filters that match the parameters within the template. These parameters might include keywords, email size, or sender domain.
- Integrate the routing templates into the email system’s configuration settings, usually found under “rules” or “filters” in the admin console.
Once set, test the routing functionality by sending test emails that match the defined criteria. Ensure the emails are being routed correctly according to the template settings.
For advanced setups, consider automating certain routing actions using scripting languages like PowerShell for Exchange or utilizing API calls for Gmail and other email services that support custom routing functionalities. These options provide greater flexibility and control over the routing process.
To set up automated routing with templates, first, select a workflow tool that supports template integration. Customize the templates to define specific routing rules, ensuring that each document or request is directed to the correct team or department based on predefined conditions.
Designing the Template

Design templates with clear routing parameters, such as document type, priority, and department. Use conditional logic within the template to automate decision-making, reducing manual intervention and speeding up the process. The template should include paths for each possible outcome, outlining who should receive the request and when.
Testing and Optimization

After setting up your templates, test the workflow with real data to ensure routing accuracy. Track the performance of each automated route and make adjustments based on bottlenecks or inefficiencies. Keep refining the templates to adapt to shifting business needs, ensuring that the routing process remains smooth and fast.
Start by mapping out the priority levels and the associated escalation paths for each case. Assign clear indicators within the template to differentiate low, medium, and high-priority scenarios. These can be visual cues, such as color codes or flag icons, that help identify urgency at a glance.
Handling Different Priority Levels

For high-priority cases, ensure that the template includes sections that demand immediate attention, such as quick response options and direct contacts. Keep these fields concise but comprehensive to facilitate fast action. For lower priority levels, reduce the complexity by limiting fields to only the most necessary information. This makes it easier for staff to manage and prioritize without unnecessary details clogging the process.
Customizing Escalation Paths
Tailor the escalation paths to reflect the urgency and complexity of each case. In high-priority situations, provide direct links to senior management or specialized departments. For medium-priority cases, allow routing through intermediate teams who can handle most issues but with the option to escalate if necessary. For low-priority cases, include self-service options or automatic replies to manage expectations and reduce workload on support teams.
| Priority Level | Escalation Path | Template Adjustments |
|---|---|---|
| High | Direct to Senior Management | Highlighted fields, immediate actions |
| Medium | Intermediate Team | Moderate complexity, escalation option |
| Low | Automated Reply/Self-Service | Minimal details, quick closure |
Verify that all template variables are correctly mapped. Incorrect or missing variable assignments often lead to broken templates. Check for typos and ensure the variable names match the expected values from the data source.
Ensure proper syntax within the template files. Misplaced brackets or commas can prevent templates from rendering correctly. Review the syntax, especially if there are nested conditions or loops in the configuration.
Check for compatibility between the template structure and the underlying system. Sometimes template engines update, which may cause incompatibility with older versions of template configurations. Always test the template after any system updates or changes.
Monitor for excessive complexity in template logic. Over-complicated conditions or nested loops can result in slow performance or errors. Simplify logic where possible to improve template rendering time and avoid potential issues.
Inspect the template for missing or incorrect file references. If the template relies on external files (like CSS or JavaScript), ensure they are correctly linked and available. Broken file paths can cause incomplete or distorted template displays.
Review permission settings for template files and directories. Insufficient file permissions can prevent templates from loading or saving changes. Confirm the correct permissions are set for the template files on the server.
Cross-check template variables with the data being passed. Mismatches between the expected data type (string, integer, etc.) and the variable type in the template can lead to rendering errors. Ensure that data is being passed correctly from the source.
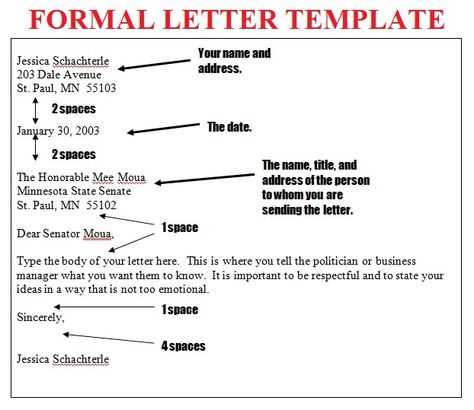
Ensure that your letter routing templates are clear and concise to avoid confusion. Start by organizing key components in a structured order, such as recipient details, subject, and body of the letter. This helps streamline the process, allowing for faster identification of necessary sections.
Template Structure
Place the recipient’s name, address, and contact information at the top, followed by the sender’s details. Align the subject line to stand out, making it easily identifiable. Keep the body short and precise, using bulleted or numbered lists for clarity when listing items or instructions.
Consistency in Layout
Use uniform margins, font styles, and spacing for readability. Avoid using overly decorative fonts that might distract from the message. This keeps the template looking professional and allows the reader to focus on the content rather than the design.