Shipping letter of instruction template
Creating a Shipping Letter of Instruction (SLI) is a straightforward task that requires clear communication. A well-structured template helps streamline the process, ensuring that all necessary details are included. This document outlines shipping instructions for freight forwarders or carriers, detailing specific requirements for transporting goods efficiently and safely.
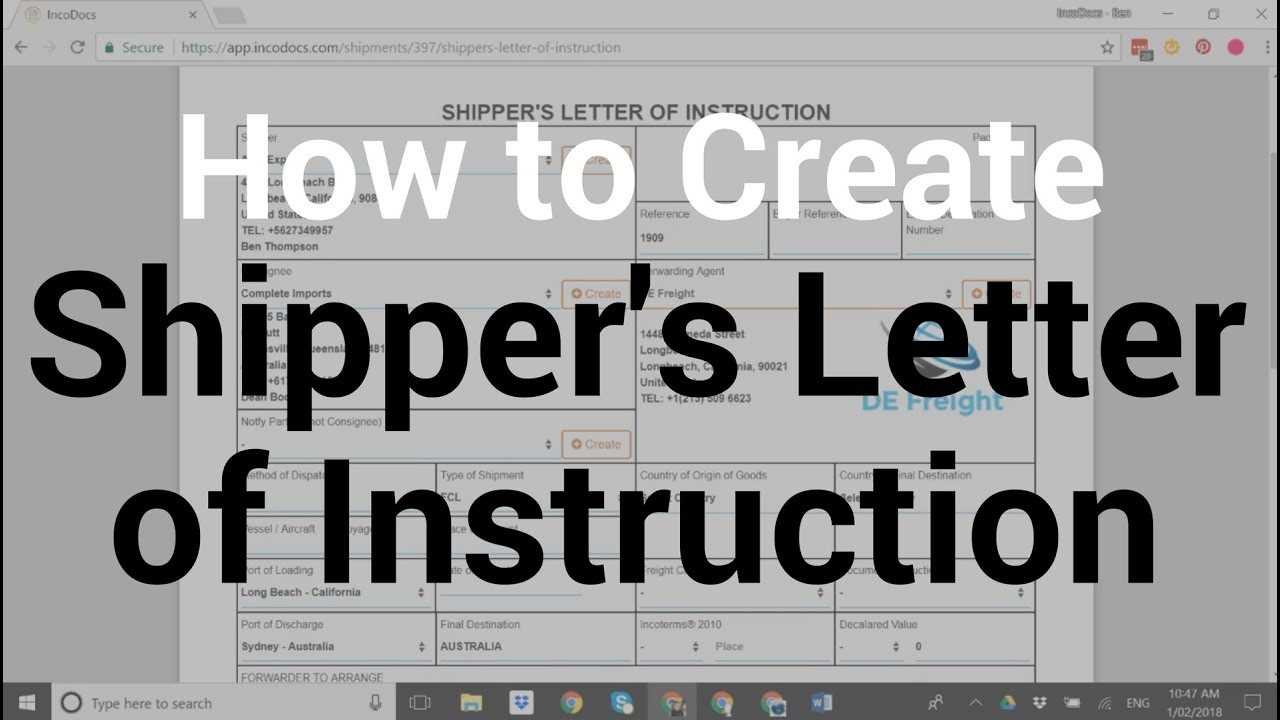
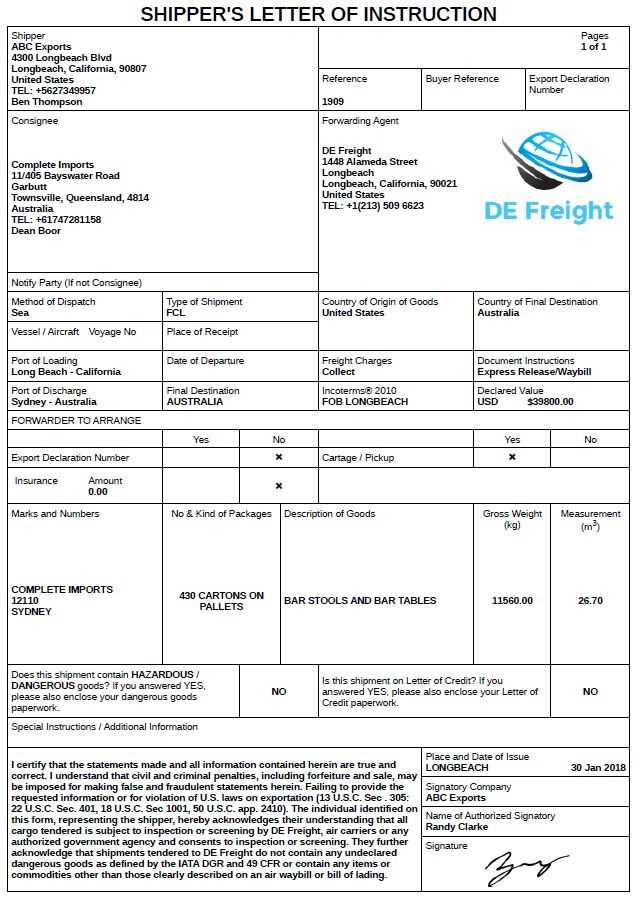
Start with the sender’s information, such as the company name, address, and contact details. This ensures that the recipient can easily reach out if needed. Follow with the consignee’s details, which may include similar information or specific instructions for receiving the shipment.
Include the shipment details next, such as the type of goods, quantity, and preferred mode of transport. Be precise about the packaging requirements, weight, and dimensions. If there are any special handling instructions or restrictions, clearly outline them to avoid any delays.
Finally, provide the payment terms, whether the cost will be prepaid or collected, and any additional charges or conditions. By organizing these elements, you create a template that ensures both sender and receiver are on the same page regarding the shipment’s details.
Here are the revised lines without unnecessary repetition:
Make sure to include clear shipping instructions in your letter. Avoid redundant phrases that can confuse the reader. For instance, instead of repeating “please send” and “kindly dispatch” multiple times, use one clear directive. Precision is key.
Use concise wording to ensure clarity. Replace lengthy sentences with simpler, direct ones. For example, instead of saying, “We would be grateful if you could provide an update,” just say, “Please provide an update.” This eliminates excess verbiage and focuses on the main action.
Keep the tone polite yet straightforward. Avoid using overly formal or overly casual language. A simple “Thank you for your cooperation” is sufficient without the need for embellishments.
For the section on cargo handling, avoid repeating details such as “please ensure careful handling” and “please take extra care” in different parts. One well-placed request covers it all. Ensure it’s clear, direct, and professional.
Finally, revise any sections where the same point is made multiple times. If the instructions for delivery are clear, there’s no need to restate them in various ways. Efficiency in wording helps streamline communication and makes the letter easier to understand.
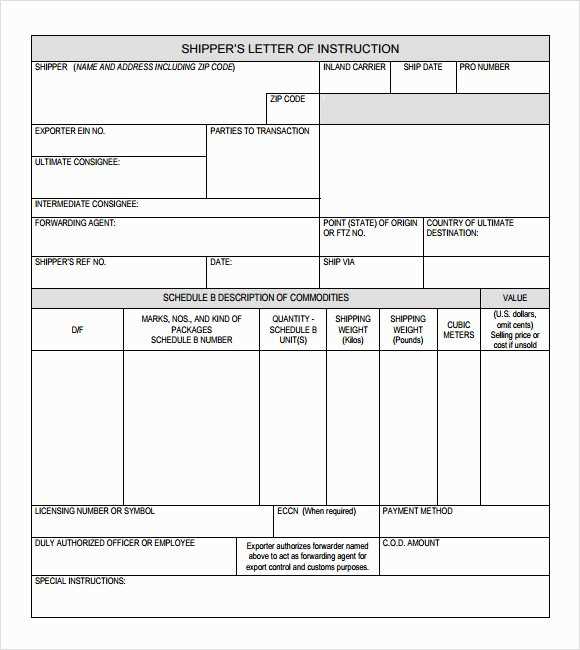
- Shipping Letter of Instruction Template
To create an effective Shipping Letter of Instruction, include the following details:
- Shipper’s Information: List the shipper’s name, address, and contact number. If needed, provide packaging instructions or any specific details about the items being shipped.
- Consignee’s Information: Include the consignee’s full name, address, and phone number. If there are any delivery instructions, such as preferred delivery times or locations, be sure to mention them.
- Carrier Information: Provide the carrier’s name, address, and phone number. If there are any specific handling requirements or preferred transport routes, include them here.
- Shipment Details: Include shipment methods (air, sea, or road) and any special handling instructions. This should also cover fragile or hazardous materials if applicable.
- Item Description: Clearly describe the items being shipped, including quantity, weight, dimensions, and packaging details. If applicable, include any handling instructions for fragile or perishable goods.
- Customs Documentation: If shipping internationally, mention any customs documents needed, such as invoices, certificates of origin, or export declarations.
- Payment Terms: Specify who is responsible for the shipping fees and whether these costs will be paid upfront or on delivery.
- Signature and Authorization: Include a space for the shipper’s signature or a representative’s authorization, along with the contact details for follow-up.
This template ensures all parties involved are on the same page and helps avoid delays or misunderstandings during the shipping process.
Begin with a clear header that identifies the purpose of the letter. Include the shipment details, such as the shipping date, reference number, and the sender and recipient information. This ensures that all involved parties know exactly what shipment the instructions pertain to.
Next, provide specific details about the shipment itself. This should include the type of goods being shipped, their weight, dimensions, and any special handling instructions. If applicable, mention any required packaging or labeling standards that must be followed.
Clarify the shipping method. Specify whether the goods will be shipped by air, sea, or land, and include any carrier details. It’s also helpful to include the agreed-upon delivery terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) to ensure everyone is on the same page regarding responsibilities for shipping costs and insurance.
Indicate the expected delivery timeline. Provide clear dates for departure, expected arrival, and any other relevant milestones, such as customs clearance. This helps to prevent confusion or delays.
List all parties responsible for the shipment. This includes the consignee, the shipper, and any third-party logistics providers involved in the transportation. Make sure each party knows their role and the actions they need to take.
End the letter with a concise summary of any critical instructions. Highlight any special requests, such as the need for temperature-controlled transport, or if the goods require specific documentation (like certificates of origin or customs forms). Ensure that these instructions are easy to find and follow.
Finally, provide contact details in case any clarification is needed. This allows recipients to reach out quickly if they have any questions or issues during the shipping process.
Make sure to include the following key details in your instruction letter to ensure clarity and avoid confusion:
- Shipper’s Details: Include the full name, address, and contact information of the shipper. This establishes clear communication lines.
- Consignee’s Information: Provide the name, address, and contact number of the consignee. This ensures the cargo reaches the right recipient.
- Vessel and Voyage Information: Specify the vessel name, voyage number, and estimated departure and arrival dates. This helps with tracking and managing logistics.
- Cargo Details: List the description of the goods, including the type, quantity, weight, and packaging method. This prevents misunderstandings during shipment.
- Customs Requirements: Include any relevant documentation, such as invoices or permits, to meet customs regulations.
- Delivery Instructions: Mention any specific delivery requirements or handling instructions, such as storage conditions or unloading details.
- Special Instructions: Provide any additional information regarding the cargo’s handling, insurance, or documentation needs.
Format and Signature
Ensure that the letter is clearly formatted, with easy-to-read sections and bullet points. Include a signature at the end to confirm authenticity.
Be clear about the details of the shipment. Providing vague or incomplete information can cause confusion and delays. Ensure that every required field, such as the consignee’s address, cargo description, and shipping instructions, is filled in accurately.
Don’t forget to double-check the shipping method. Misunderstanding or skipping the preferred shipping method can lead to unnecessary costs or delayed delivery. Make sure to specify whether it’s air, sea, or ground transportation.
Incorrect Consignee Details
Verify the consignee’s contact details. Incorrect or outdated contact information can result in missed communications or misdirected shipments. It’s a simple yet important step to avoid issues down the road.
Inaccurate or Missing Documentation
Ensure all necessary documents are included, like customs declarations or invoices. Missing paperwork can halt the shipment process or lead to fines. Keep track of all required forms and submit them alongside the shipping letter.
Adjusting a Shipping Letter of Instruction (LOI) for different scenarios requires understanding the specifics of each situation and making relevant changes to ensure smooth execution. Here’s how you can modify your template for various shipping cases:
1. International Shipments

- Include the correct Incoterms (e.g., CIF, FOB) to define the responsibilities of each party.
- Specify the customs clearance instructions, including the necessary documentation for import and export compliance.
- Be clear about the currency for transactions and include any currency conversion details if applicable.
- Ensure accurate port of origin and destination details, including contact information for both parties in case of issues.
2. Hazardous Materials Shipping
- Clearly state the classification of hazardous materials (e.g., UN number, proper shipping name, and hazard class).
- Ensure compliance with the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) code or other relevant regulations.
- Indicate the required safety measures, such as labeling, packaging, and handling instructions.
- Provide emergency response contact information and any specific instructions related to the storage or transportation of hazardous goods.
3. Temperature-Controlled Shipments

- Specify temperature ranges and the type of equipment required (e.g., refrigerated containers or insulated packaging).
- Outline the expected temperature monitoring processes and the frequency of checks during transit.
- Indicate contingency plans in case of temperature deviations, including actions to take if the temperature fluctuates outside the acceptable range.
4. Expedited Shipments
- Ensure that the shipping schedule reflects expedited timelines, and confirm delivery deadlines.
- Note the use of premium carriers or services that guarantee quicker delivery.
- Provide clear instructions for any urgent paperwork or documentation that needs to be processed quickly.
By customizing the Shipping Letter of Instruction to address the unique needs of each shipping situation, you can avoid delays and ensure the efficient movement of goods. Tailoring the details to the type of shipment increases accuracy and reduces the potential for errors in the process.
Include all relevant information required by local, international, and industry-specific regulations. Verify that the shipping instruction letter reflects accurate details regarding shipment, including product classification, destination, and transport method, in accordance with applicable laws.
Check if your letter complies with customs regulations. Ensure that it includes proper declarations and documentation, such as harmonized codes, tariff classifications, and any other information that may be necessary for customs clearance.
Incorporate terms and conditions that reflect compliance with shipping laws, such as those pertaining to safety, insurance, and liability. Specify who is responsible for particular charges or actions in case of issues with the shipment.
Ensure that all references to international shipping standards, such as Incoterms, are correctly used and clearly defined to avoid confusion in legal interpretations. Verify that these terms align with the obligations and rights of both parties involved in the transaction.
Consult a legal expert to double-check compliance with regulations such as export controls, sanctions, or other restrictions that may apply to the shipment. Make sure the letter does not unintentionally violate any trade restrictions or embargoes.
Update the letter regularly to reflect any changes in relevant laws or industry practices. Always maintain consistency with the latest legal requirements and best practices to avoid potential legal disputes or delays in shipping.
Double-check all the shipment details, including the recipient’s information, shipping method, and delivery address. Ensure the dates, times, and terms align with the agreement and any specific instructions from the customer.
Verify the accuracy of the cargo description, weight, and volume. Cross-reference these with the bill of lading or commercial invoice to avoid discrepancies.
Check the compliance with any regulatory requirements, such as customs documentation, export permits, or import restrictions, based on the destination country.
Ensure that the required signatures are obtained. This includes the shipper’s and any other parties involved in the shipping process.
Review the payment details and ensure that the shipping charges, duties, and taxes are correctly calculated and covered. Address any discrepancies before finalizing the document.
Confirm the inclusion of any specific instructions, such as handling requirements, special delivery notes, or hazardous material declarations, if applicable.
Finalize the letter by confirming that all fields are complete and correctly formatted. Save a copy for records, and then forward it to the relevant parties for approval or action.
Make sure the Letter of Instruction (LOI) clearly states the shipping instructions with all necessary details to avoid confusion. Every section should be organized logically, ensuring the recipient can easily understand each point.
Start with a brief introduction to the shipment, specifying the cargo, sender, and recipient details. Follow this by providing precise instructions related to the shipment, such as packaging requirements, preferred carriers, and any special handling instructions. Include the delivery terms and any deadlines to ensure smooth execution.
In addition, always provide a contact section in case of issues. This will allow both the sender and recipient to resolve problems quickly if any arise during the shipping process.
The Letter of Instruction should also mention any necessary legal terms or documentation requirements. Make sure these are clear and unambiguous to avoid delays or legal complications.
Here’s an example of how to structure your LOI:
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Sender Information | Provide full details including name, address, and contact info of the sender. |
| Receiver Information | Include the recipient’s name, address, and contact details. |
| Shipping Instructions | Specify any special shipping requirements like handling, packaging, or preferred carriers. |
| Delivery Terms | State the shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF), along with the expected delivery date. |
| Documentation | List any required documents such as bills of lading or certificates of origin. |
| Contact Information | Provide contact details for both parties to handle any shipping concerns. |
Clear communication in your LOI minimizes the chance of errors or delays. Always double-check the information to ensure accuracy before sending it.